Logistics and Supply Chain Management: 2 Key Differences

The terms “supply chain” and “logistics” are often used interchangeably, though they mean different things. To better understand the meaning of supply chain versus logistics, let’s break down both terms and look at some examples.
What is the Supply Chain?
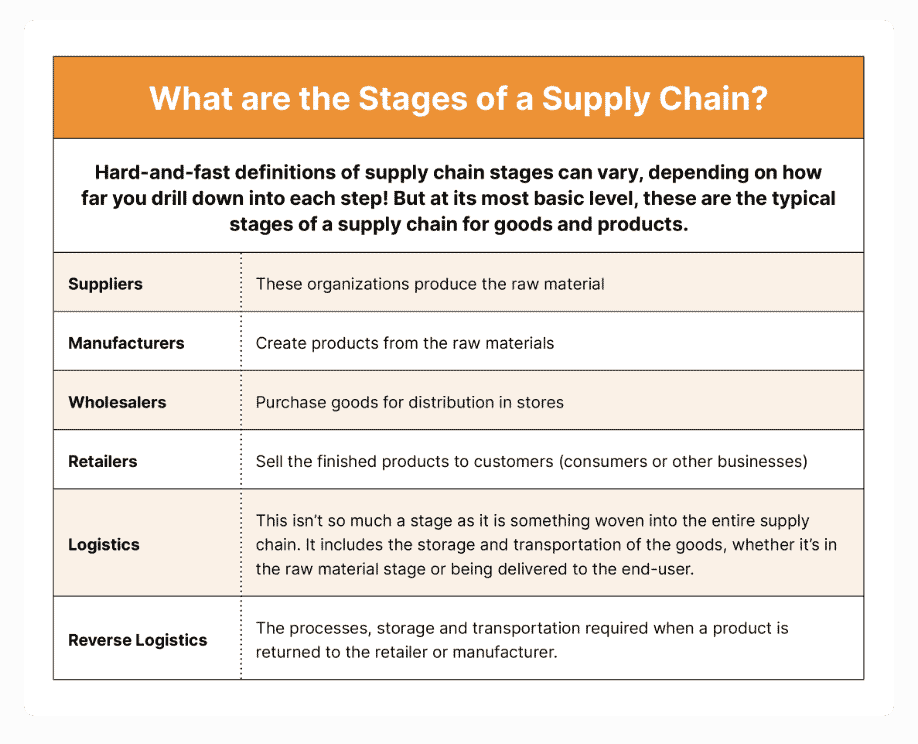
The supply chain is the entire flow of goods and services, from start to finish. Beginning with the raw material used to create a product, to the producer or manufacturer, to the transporter, seller, and everyone in between, the supply chain is the network of all those parts.
What is Supply Chain Management?
Supply chain management is simply the coordination and orchestration of the entire supply chain. Some companies or individuals may be involved with managing stages of the supply chain, while others may have responsibilities that encompass the entirety of it.
What are Logistics?
As noted above, logistics refers to everything that goes into storing or moving materials and goods within the supply chain. So if you’re not sure whether to use “logistics” or “supply chain,” think of the supply chain as the entire event required to create and deliver a product. Logistics is simply the storage and movement of that product.
What is the Role of Logistics in the Supply Chain?
Some have referred to logistics as “the foundation of the supply chain.” A logistics team is responsible for receiving and coordinating the distribution of supplies, getting the finished goods to the distribution center, managing inventory and getting a product to the retailer or customer. According to SupplyChain24/7, nearly three-quarters of logistics spending by companies is spent on transportation and inventory.
What are the Three Types of Logistics?
Logistics are typically segmented into three types: Inbound, outbound and reverse logistics.
Inbound logistics: This refers to the system and processes that move goods into the realm of a seller. It includes the transportation, storage and receiving of goods – all the internal tasks and activities that must be completed to receive a product from the manufacturer or producer.
Outbound logistics: Outbound logistics covers the processes required to get a product from a seller’s store, distribution or warehouse to the purchaser. Outbound logistics include order fulfillment, packaging, shipping and delivery.
Reverse Logistics: The transportation and storage tasks required to manage a product that’s returned to the seller or manufacturer; essentially, when a sale is “reversed.” Reverse logistics also include the steps a customer must take to return a product and get it repaired, replaced, or refunded/credited.
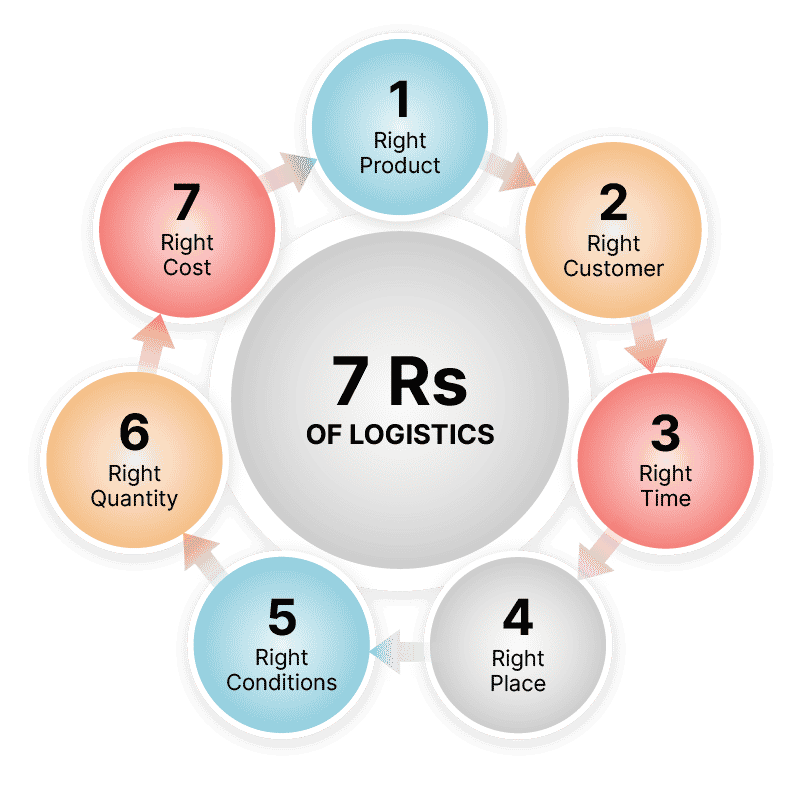
What are the 7 Rs of Logistics?
To better understand the role of logistics, many in the industry describe the 7 Rs that make up this broad part of the supply chain. The 7 Rs of Logistics are…
Getting the right product, in the right quantity, in the right condition, at the right place, at the right time, to the right customer, at the right price.
The 7 Rs clarify the end-to-end orchestration required to get a product to a customer. And it makes one appreciate the enormous coordination behind the scenes that few of us think about when we’re making a purchase!
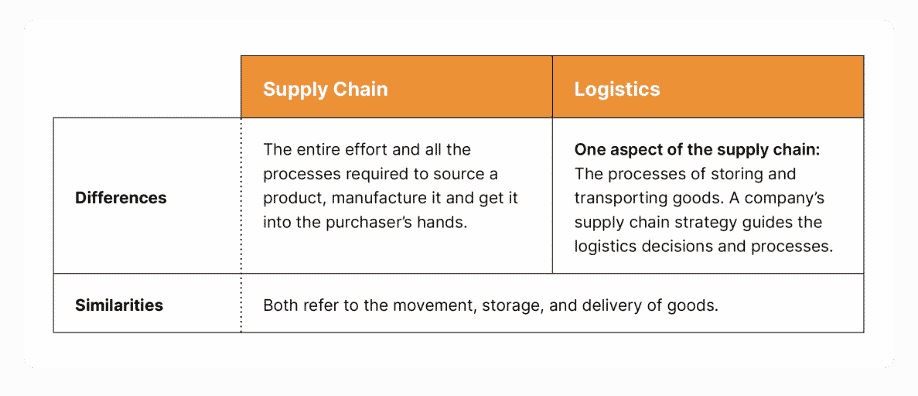
What are the Differences between Logistics and the Supply Chain?
Recapping what was discussed above, here is a quick reference table to compare and contrast the supply chain versus logistics.
Frequently Asked Questions about the Supply Chain
1. What is the Most Important Part of the Supply Chain?
It’s hard to name one part of the supply chain that’s the most important because if any part of it fails, the entire supply chain is at risk.
Perhaps a better question is: What part of the supply chain is most underutilized?
Here at ReverseLogix, we routinely work with companies that have ignored their reverse logistics process for far too long. The result is costly product returns and frustrated customers. It’s essential to make reverse logistics a core competency of your supply chain operations.
2. How does Reverse Logistics Improve a Supply Chain?
Reverse logistics is the key to anticipating, managing and, ideally, preventing potential runaway aftermarket issues. But it’s also a highly effective means for improving the management of your supply chain and maximizing business performance.
Good reverse logistics management helps reduce the number and cost of returns by pinpointing and resolving issues that are causing customers to return an item. Go here to learn more ways that reverse logistics impacts the supply chain.
3. What are the 5 Rs of Returns Management?
Returns management is a term that covers many facets of a product’s return journey, so it can be overwhelming to figure out which aspects to prioritize. That’s why we’ve put together the “five Rs” that are generally considered to be the foundational components of returns management. Let’s take a look at each one.
